Info
&
Insights
What It Takes to Implement a Safety Management System (SMS)
December 11, 2024

Implementing a Safety Management System (SMS) is a transformative step for any aviation operator. It establishes a systematic approach to managing safety, including necessary organizational structures, accountabilities, policies, and procedures. However, it requires careful planning, commitment from all levels of the organization, and adherence to industry standards. Here’s a breakdown of the essential components to consider when implementing an SMS, along with tips for navigating the process effectively.
Choosing Between a Paper-Based or Software-Based SMS
One of the first decisions operators must make is whether to adopt a traditional paper-based SMS or a software-based system.
- Paper-Based SMS: Ideal for small operators with limited resources or straightforward operations. It’s cost-effective upfront but can be labor-intensive for tracking data and generating reports
- Software-Based SMS: Provides scalability, streamlined data collection, and reporting features. While the initial investment may be higher, it’s often more efficient in the long term
The choice depends on your operation’s size, complexity, and budget.
Development of an SMS Manual
The SMS manual serves as the foundation of your program. It outlines policies, processes, roles, and responsibilities for everyone in the organization. A good manual should be:
- Tailored to your organization
- Aligned with ICAO, FAA, or other regulatory requirements
- A living document that evolves with your operation
Defining Key Roles: Accountable Executive, Managers, and Frontline Staff
- Accountable Executive: This person has ultimate responsibility for the SMS. Their commitment to safety sets the tone for the organization
- Managers: Act as the bridge between the executive and frontline staff, ensuring processes are followed and risks are managed
- Frontline Staff: Integral to hazard reporting and operational safety, as they are often the first to spot safety concerns
Ensuring all roles are clearly defined and understood is crucial for SMS success.
Developing a Hazard Reporting System
Encouraging employees to report hazards is a cornerstone of SMS. To create an effective system:
- Ensure anonymity and confidentiality when appropriate
- Make reporting simple and accessible
- Foster a non-punitive reporting culture
Safety Risk Management (SRM) and Risk Assessment Process
SRM involves identifying hazards, assessing risks, and implementing mitigations. Developing a robust SRM process includes:
- Standardized risk assessment tools
- Clear criteria for assessing severity and likelihood
- Documentation of mitigations and follow-up actions
Providing Safety Communications to the Team
Regular communication ensures that safety remains a top priority. Use newsletters, safety meetings, or digital platforms to:
- Share hazard reports and lessons learned
- Highlight safety achievements
- Provide updates on SMS progress
SMS Training for All Individuals
Training is critical to understanding SMS and ensuring compliance. Training should:
- Cover roles and responsibilities for all employees
- Be tailored to different levels within the organization
- Include initial and recurrent sessions to keep safety practices fresh
Developing an Internal Audit Program
An internal audit program ensures SMS effectiveness and compliance. Elements of a strong audit program include:
- Scheduled audits to assess SMS implementation
- Clear checklists and guidelines
- Documentation and follow-up on corrective actions
Assessing Safety Culture
Safety culture is the backbone of SMS. Operators should:
- Conduct regular culture surveys
- Address gaps in trust, accountability, and communication
- Reinforce leadership’s commitment to safety
Developing Processes for Full Implementation
To ensure SMS is fully implemented:
- Integrate SMS processes into daily operations
- Use Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to monitor progress
- Review and refine processes regularly
Understanding the Timeframe
Implementing an SMS takes time and varies by organization size and complexity. While smaller operators might complete the process within 12–18 months, larger or more complex organizations might take 2–3 years. The timeframe includes:
- Initial planning and resource allocation
- Training and manual development
- Gradual integration of SMS components
Preparing for the FAA SMS Mandate
With the FAA SMS mandate looming, organizations must prioritize SMS readiness. Steps to take now:
- Assess current safety processes and identify gaps.
- Begin training employees to understand SMS principles.
- Allocate resources, including budget and personnel, to support SMS development.
Why Training Matters
Training is the linchpin of a successful SMS. It ensures that all personnel:
- Understand their role within the system
- Are equipped to identify and mitigate risks
- Can contribute to a culture of safety
Investing in training early not only accelerates implementation but also builds the foundation for long-term success.
Implementing an SMS is a challenging but rewarding process. By focusing on comprehensive planning, organizational commitment, and continuous improvement, operators can create a safer, more resilient aviation environment. With the FAA SMS mandate approaching, there’s no better time to begin the journey. Remember, the success of your SMS hinges on the engagement and dedication of every individual in your organization.
###
Read More
From Reactive to Proactive: Achieving a Predictive Safety Management System in a Small Flight Department
November 27, 2024

Transitioning from a reactive approach to safety management towards a proactive and predictive system is a crucial step for small flight departments seeking to enhance safety and prevent incidents before they occur. A predictive safety management system (SMS) enables organizations to identify potential risks, anticipate hazards, and implement preventive measures. In this article, we will explore key strategies to help small flight departments achieve a predictive safety management system, fostering a proactive safety culture and minimizing the likelihood of safety incidents.
Establish a Robust Reporting Culture - Develop a reporting culture that encourages employees to report safety concerns, near misses, and hazards. Implement a confidential and non-punitive reporting system that allows individuals to share information without fear of reprisal. Regularly communicate the importance of reporting and emphasize that it contributes to proactive risk mitigation and continuous improvement.
Data Collection and Analysis - Implement systems and processes to collect and analyze safety data effectively. Utilize incident reporting forms, safety surveys, and employee feedback mechanisms to gather data on potential hazards and safety-related issues. Establish a central database or safety management software to organize and analyze the collected data. Regularly review and analyze the data to identify trends, patterns, and potential risks.
Utilize Predictive Analytics - Leverage the power of predictive analytics to identify and assess potential safety risks. Analyze historical data, incident reports, and safety trends to identify leading indicators that can predict future safety issues. These leading indicators could include factors such as maintenance trends, operational deviations, or external influences. By understanding these indicators, small flight departments can take proactive measures to prevent incidents.
Utilize Predictive AnalyticsConduct Risk Assessments - Regularly conduct comprehensive risk assessments across all areas of operations. Identify potential hazards, assess their likelihood and severity, and prioritize risk mitigation strategies. Utilize risk assessment techniques such as Bow-Tie analysis, Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA), or Job Safety Analysis (JSA) to comprehensively evaluate risks and identify preventive measures.
Implement Safety Performance Monitoring - Establish key safety performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with the organization's safety goals. Develop a system to monitor and measure these KPIs regularly. Utilize tools such as dashboards or scorecards to track safety performance trends. Identify leading indicators that can provide insights into potential risks and implement proactive measures to address them.
Continuous Improvement and Learning - Embrace a culture of continuous improvement and learning within the flight department. Encourage employees to actively participate in safety-related training, workshops, and seminars. Promote a learning environment where employees can share lessons learned, best practices, and safety insights. Regularly review and update safety policies and procedures based on lessons learned and emerging industry best practices.
Collaboration and Industry Engagement - Engage in collaborations and industry partnerships to gain access to best practices and benchmark against industry standards. Participate in aviation industry associations, conferences, and forums to stay informed about the latest trends, technologies, and safety initiatives. Collaborate with other flight departments to share experiences, lessons learned, and best practices to foster a collective effort towards achieving a predictive safety management system.
Achieving a predictive safety management system is an ongoing journey for small flight departments committed to proactive risk mitigation and enhancing safety performance. By establishing a robust reporting culture, implementing effective data collection and analysis processes, utilizing predictive analytics, conducting risk assessments, monitoring safety performance, fostering a culture of continuous improvement, and engaging with the aviation industry, small flight departments can successfully transition from a reactive to a predictive safety approach. Embracing a predictive safety management system empowers organizations to identify potential risks, anticipate hazards, and implement preventive measures, ensuring the highest levels of safety and operational excellence in aviation operations.
###
Read More
Navigating the Challenges: Key Considerations for Preparing for an IS-BAO Audit
October 15, 2024

The International Standard for Business Aircraft Operations (IS-BAO) is a globally recognized set of best practices and standards for business aviation operations. Achieving IS-BAO certification demonstrates an organization's commitment to safety management and operational excellence. However, preparing for an IS-BAO audit can be a complex process that requires careful planning and attention to detail. In this article, we will discuss some primary issues to consider when preparing for an IS-BAO audit.
Understanding the IS-BAO Standards
The first and foremost step is to thoroughly understand the IS-BAO standards and requirements. Familiarize yourself with the IS-BAO manual, which outlines the various elements of the safety management system (SMS) and operational practices that need to be in place. Gain a comprehensive understanding of the processes, policies, and procedures specific to your organization's operations and align them with the IS-BAO standards.
Documentation and Record-Keeping
Documentation is a critical aspect of an IS-BAO audit. Ensure that all required documents are up to date, easily accessible, and stored in an organized manner. This includes safety policies, procedures, risk assessments, training records, incident reports, and maintenance documentation. Implement robust record-keeping practices to demonstrate compliance and provide evidence of the effectiveness of your SMS.
Implementation of Safety Management System (SMS)
The IS-BAO audit focuses heavily on the effectiveness of the SMS. It is essential to demonstrate that your organization has a comprehensive SMS in place and that it is effectively implemented throughout all levels of the organization. Ensure that safety responsibilities are clearly defined, safety accountabilities are established, and that there is a systematic approach to hazard identification, risk assessment, risk mitigation, and continuous improvement.
Employee Training and Competency
The competency and training of personnel play a significant role in IS-BAO compliance. Ensure that employees receive appropriate training and that their competencies are regularly assessed. Keep records of training sessions, qualifications, and certifications. Develop a robust training program that covers all relevant aspects of the IS-BAO standards and ensures that employees are aware of their safety-related responsibilities.
Gap Analysis and Internal Audits
Conducting a thorough gap analysis against the IS-BAO standards is crucial in identifying areas where your organization may fall short. This process will help you identify gaps and develop an action plan to address them before the actual audit. Additionally, regular internal audits should be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance and identify any non-conformities or areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement Culture
IS-BAO emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement. Demonstrate that your organization has a culture of learning, feedback, and proactive improvement. Regularly review safety performance indicators, analyze safety data, and implement corrective actions when necessary. Show evidence of a feedback loop that fosters communication and collaboration to drive continuous improvement in safety practices.
Preparing for an IS-BAO audit requires diligent planning, attention to detail, and a strong commitment to safety management practices. By understanding the IS-BAO standards, maintaining comprehensive documentation, implementing an effective SMS, ensuring employee training and competency, conducting gap analyses and internal audits, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can navigate the challenges of an IS-BAO audit successfully. Achieving IS-BAO certification not only demonstrates a commitment to safety but also enhances operational excellence and elevates the overall standard of business aviation operations.
###
Read More
Integrating Safety Management System Case Studies into Flight Training: Enhancing Safety Awareness and Learning
September 18, 2024

Effective training plays a critical role in maintaining a strong safety culture within flight organizations. To ensure continuous improvement and promote safety awareness, integrating real-life case studies from the Safety Management System (SMS) into initial and recurrent training is highly beneficial. These case studies provide valuable insights into past incidents, hazards, and lessons learned, enabling flight crews and personnel to enhance their safety knowledge and decision-making abilities. In this article, we will explore the steps involved in integrating SMS case studies into flight training, fostering a proactive safety mindset and improving overall operational safety.
Identify Relevant and Impactful Case Studies
Begin by identifying relevant and impactful case studies from your organization's SMS. Look for incidents, near misses, or hazardous situations that highlight important safety lessons and have the potential to resonate with trainees. Focus on case studies that cover a range of topics, such as crew resource management, emergency procedures, maintenance-related incidents, and human factors, to provide a comprehensive perspective on safety considerations.
Understand the Context and Root Causes
Thoroughly analyze each case study to understand the context, contributing factors, and root causes of the incident or hazard. Identify the underlying safety principles, regulatory requirements, and standard operating procedures that were relevant to the situation. This analysis will provide a deeper understanding of the challenges faced and the importance of adherence to safety protocols.
Develop Case Study Presentations
Create engaging and interactive case study presentations for training sessions. Structure the presentations to include key details, such as the background of the incident, sequence of events, human factors involved, and the consequences or outcomes. Use visuals, diagrams, and audiovisual materials to enhance the learning experience and promote better retention of information.
Facilitate Group Discussions and Analysis
Encourage active participation and facilitate group discussions during case study sessions. Encourage trainees to share their thoughts, experiences, and insights related to the case study. Ask open-ended questions that encourage critical thinking and promote a deeper understanding of the safety principles and practices involved. This interactive approach fosters a collaborative learning environment and allows trainees to learn from each other's perspectives.
Relate Case Studies to Procedures and Policies
Highlight how the case studies relate to the organization's procedures, policies, and safety management systems. Emphasize the importance of following established protocols, reporting hazards, and adhering to safety regulations. Help trainees understand how their actions and decisions can have a direct impact on safety outcomes, reinforcing the relevance of the case studies to their day-to-day operations.
Extract Key Lessons Learned
Extract key lessons learned from each case study and discuss their implications for safe operations. Analyze the potential preventive measures and mitigation strategies that could have been employed to avoid or minimize the impact of the incident. Encourage trainees to think critically about how they can apply these lessons to their own roles and responsibilities.
Incorporate Case Studies into Scenario-Based Training
Integrate case studies into scenario-based training exercises to provide practical application opportunities. Develop simulations or role-playing exercises that allow trainees to experience similar scenarios firsthand and practice their decision-making skills in a safe environment. This hands-on approach reinforces the lessons learned from the case studies and enhances their ability to apply safety principles in real-world situations.
Continuous Learning and Review
Promote a culture of continuous learning by periodically reviewing and revisiting the case studies with trainees. Encourage ongoing discussion and reflection on the key lessons learned. Regularly update the case studies with new incidents or emerging safety issues to keep the training content relevant and up to date.
Integrating case studies from the Safety Management System (SMS) into flight training is a powerful way to enhance safety awareness and improve decision-making capabilities within a flight organization. By identifying relevant case studies, analyzing root causes, facilitating group discussions, relating them to procedures and policies, extracting key lessons learned, incorporating them into scenario-based training, and fostering a culture of continuous learning, flight organizations can maximize the impact of their training programs. The integration of SMS case studies provides a practical and engaging approach to improving safety practices, enabling flight crews and personnel to make informed decisions and effectively manage risks in their day-to-day operations.
###
Read More
Executive Leadership and the Vital Role in Supporting the Safety Management System in a Flight Organization
September 3, 2024

In the aviation industry, executive leadership plays a critical role in shaping the safety culture and ensuring the success of the Safety Management System (SMS) within a flight organization. The commitment and support of top-level executives are crucial for establishing a robust safety culture, promoting effective safety practices, and ensuring regulatory compliance. In this article, we will explore the importance of executive leadership in supporting the Safety Management System and its impact on the overall safety performance of a flight organization.
Setting the Tone at the Top:
Executive leaders have the power to set the tone for safety within the organization. By consistently demonstrating a strong commitment to safety, executives create a culture where safety becomes a core value and an integral part of the organization's DNA. Through their actions and communication, leaders establish safety as a top priority and inspire employees at all levels to prioritize safety in their daily operations.
Establishing Clear Safety Policies and Objectives:
Executive leaders are responsible for establishing clear safety policies and objectives that align with the organization's vision and values. They should ensure that safety objectives are clearly communicated to all employees and integrated into the organization's strategic planning processes. By setting measurable safety goals, leaders provide a framework for continuous improvement and guide the organization towards achieving optimal safety outcomes.
Allocating Adequate Resources:
Supporting the Safety Management System requires the allocation of adequate resources, including personnel, technology, training, and financial investments. Executive leaders must prioritize safety in resource allocation decisions, ensuring that the necessary tools and resources are available to effectively implement and maintain the SMS. By allocating sufficient resources, leaders demonstrate their commitment to safety and provide the foundation for a robust safety program.
Empowering Safety Managers and Personnel:
Executive leaders should empower safety managers and personnel by granting them the authority and autonomy necessary to implement the SMS effectively. They should encourage open communication, active participation, and collaboration among safety professionals and employees at all levels. By fostering an environment where individuals feel empowered to report safety concerns and contribute to safety initiatives, leaders create a proactive safety culture that supports the success of the SMS.
Leading by Example:
Executive leaders have a significant influence on the behavior and attitudes of employees throughout the organization. By consistently demonstrating safety-conscious behaviors and adhering to safety protocols, leaders set a positive example for others to follow. When executives prioritize safety in their decision-making and actively engage in safety initiatives, it reinforces the importance of safety throughout the organization and encourages employees to do the same.
Regular Communication and Engagement:
Effective communication is vital in promoting a safety culture and ensuring alignment with the SMS. Executive leaders should regularly communicate safety messages, updates, and achievements to employees through various channels, such as newsletters, meetings, and company-wide communications. They should engage with employees at all levels, listen to their safety concerns, and actively seek their input and feedback. This inclusive approach creates a sense of ownership and fosters a collaborative safety culture.
Continuous Improvement and Learning:
Executive leaders should encourage a culture of continuous improvement and learning within the flight organization. They should support the ongoing review and evaluation of the SMS, facilitate lessons learned from safety incidents or near misses, and promote the adoption of best practices and industry standards. By promoting a learning mindset and embracing opportunities for improvement, leaders contribute to the development of a proactive safety management system.
Executive leadership plays a pivotal role in supporting the Safety Management System within a flight organization. Through their commitment, clear communication, resource allocation, empowerment of safety personnel, leading by example, regular engagement, and dedication to continuous improvement, leaders establish a strong safety culture that permeates throughout the organization. When executives prioritize safety, employees at all levels are inspired to do the same, resulting in a safer and more successful aviation operation. The collective efforts of executive leaders and employees, united in their commitment to safety, lead to improved safety performance, regulatory compliance, and a positive safety culture within the flight organization.
###
Read More
The Integral Role of Organizational Culture in Aviation Safety
August 5, 2024

When discussing aviation safety, the focus often gravitates toward advanced technologies, rigorous training programs, and comprehensive regulatory frameworks. However, one crucial element that sometimes escapes the limelight is the cultural attributes of an organization. The culture within an aviation organization plays a fundamental role in shaping safety outcomes, influencing everything from day-to-day operations to long-term strategic decisions.
Defining Organizational Culture in Aviation
Organizational culture encompasses the shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that characterize an organization. In the context of aviation, it includes attitudes toward safety, adherence to protocols, communication practices, and the overall mindset of employees towards risk and accountability. A robust safety culture is not merely a set of policies and procedures but an ingrained ethos that prioritizes safety above all else.
The Impact of Culture on Safety
Attitude Towards Safety Compliance
In a strong safety culture, compliance with safety regulations is viewed as a non-negotiable priority. Employees at all levels understand the importance of following established safety procedures and recognize their role in maintaining a safe operational environment. This contrasts sharply with organizations where safety compliance is seen as a burdensome formality, often leading to corners being cut and safety measures being overlooked.
Communication and Reporting
Effective communication is a hallmark of a positive safety culture. In such environments, employees feel comfortable reporting safety concerns and incidents without fear of retribution. This open reporting culture allows organizations to identify and address potential hazards proactively, fostering continuous improvement in safety practices. Conversely, in a culture where communication is stifled, critical safety issues may go unreported, increasing the risk of accidents.
Leadership Commitment
Leadership plays a pivotal role in shaping and reinforcing safety culture. When leaders demonstrate a genuine commitment to safety, it permeates throughout the organization. This commitment can be reflected in the allocation of resources for safety programs, the establishment of clear safety policies, and the active involvement of leadership in safety initiatives. Leaders who prioritize safety set a powerful example for the entire organization, reinforcing the importance of safety at every level.
Empowerment and Accountability
A safety-oriented culture empowers employees to take ownership of safety. This involves not only adhering to safety protocols but also actively participating in safety initiatives and being vigilant in identifying potential risks. When employees feel accountable for safety, they are more likely to take proactive measures to mitigate hazards and contribute to a safer work environment.
Continuous Learning and Improvement
Organizations with a strong safety culture are committed to continuous learning and improvement. They recognize that safety is an evolving domain and that staying ahead of potential risks requires ongoing training, regular safety audits, and the adoption of best practices. This mindset fosters an environment where employees are encouraged to learn from incidents and near-misses, driving continuous enhancements in safety performance.
Building and Sustaining a Safety Culture
Developing a robust safety culture requires a concerted effort and a long-term commitment.
Here are some key strategies:
Leadership Engagement - Leaders must be visibly and actively engaged in promoting safety. This includes regular communication about safety priorities, participating in safety training, and leading by example.
Training and Education - Comprehensive training programs that emphasize the importance of safety and equip employees with the knowledge and skills to maintain a safe environment are essential. Continuous education ensures that safety remains a top priority.
Open Communication Channels - Establishing clear and open channels for reporting safety concerns and incidents encourages transparency and ensures that potential risks are promptly addressed.
Recognition and Rewards - Recognizing and rewarding employees for their contributions to safety can reinforce positive behaviors and motivate others to prioritize safety.
Regular Audits and Reviews - Conducting regular safety audits and reviews helps identify areas for improvement and ensures that safety practices are consistently applied.
The cultural attributes of an organization are inextricably linked to its safety performance. A strong safety culture, characterized by leadership commitment, open communication, employee empowerment, and a continuous improvement mindset, is essential for achieving and maintaining high safety standards in aviation. By prioritizing safety culture, organizations can create an environment where safety is not just a policy but a deeply embedded value that guides every action and decision.
###
Read More
Avoiding Common Pitfalls: Top 10 Errors When Developing a Safety Management System
July 17, 2024

Developing a robust safety management system (SMS) is crucial for aviation operators to ensure the highest standards of safety and regulatory compliance. However, the process of establishing an effective SMS can be complex, and operators often encounter common errors that hinder their efforts. In this article, we will explore the top 10 errors operators make when developing a safety management system and provide insights on how to avoid them.
#1 - Lack of Leadership Commitment
One of the most significant errors is insufficient leadership commitment to the SMS. Without the active involvement and support of senior management, the SMS may not receive the necessary resources, attention, and commitment to drive its successful implementation. Leadership should demonstrate a strong safety culture and provide clear guidance and support throughout the SMS development process.
#2 - Inadequate Risk Assessment
Failing to conduct comprehensive and ongoing risk assessments is another common error. Risk assessment is the foundation of an effective SMS, as it identifies potential hazards and assesses their associated risks. Operators should utilize appropriate risk assessment methods, involve relevant personnel, and regularly review and update risk assessments to ensure that all significant risks are identified and mitigated.
#3 - Insufficient Employee Involvement
Neglecting to involve employees throughout the SMS development process is a common mistake. Employees possess valuable knowledge and frontline experience, and their involvement enhances the effectiveness and acceptance of the SMS. Engage employees through regular communication, training programs, safety committees, and feedback mechanisms to ensure their active participation in developing and implementing the SMS.
#4 - Poor Documentation and Procedures
Inadequate documentation and poorly defined procedures can hinder the effectiveness of an SMS. Clear, concise, and user-friendly documentation is essential for employees to understand and follow safety procedures. Develop standardized templates, guidelines, and checklists to ensure consistent documentation practices. Regularly review and update documentation to reflect changes in regulations or operational requirements.
#5 - Lack of Training and Competency
Failing to provide sufficient training and competency assessment for employees is a critical error. Training should align with the SMS requirements and the specific roles and responsibilities of each employee. Implement a comprehensive training program that covers safety policies, procedures, risk management, and reporting protocols. Regularly assess and verify employee competency to ensure a competent and well-prepared workforce.
#6 - Ineffective Safety Reporting and Investigation
A common error is the absence of an effective safety reporting and investigation system. A robust reporting system encourages the reporting of safety concerns, incidents, and near misses. Establish a non-punitive reporting culture and a confidential reporting system that encourages open communication and ensures anonymity if desired. Investigate incidents thoroughly to identify root causes and implement corrective actions.
#7 - Inadequate Performance Monitoring and Measurement
Failing to establish mechanisms for performance monitoring and measurement is a significant error. Metrics and key performance indicators or safety performance indicators (KPIs or SPIs) are essential for tracking the effectiveness of the SMS and identifying areas for improvement. Define relevant KPIs/SPIs, establish data collection processes, and regularly analyze performance trends to evaluate the SMS's effectiveness and implement necessary adjustments.
#8 - Insufficient Communication and Awareness
Neglecting to effectively communicate and raise awareness about the SMS within the organization is a common mistake. Ensure that all employees are aware of the SMS, its objectives, and their roles and responsibilities. Utilize various communication channels, such as meetings, newsletters, and intranets, to provide regular updates, share safety-related information, and reinforce the importance of safety in daily operations.
#9 - Lack of Continuous Improvement
Failure to foster a culture of continuous improvement is an error that limits the SMS's long-term effectiveness. Encourage the identification and implementation of corrective actions based on safety data analysis, audits, and employee feedback. Regularly review and update the SMS to reflect changes in regulations, lessons learned, and emerging industry best practices.
#10 - Inadequate Management of Change
Overlooking the importance of managing change effectively is a common error. The SMS should be adaptable to organizational changes, such as new processes, equipment, or personnel. Implement a structured change management process that identifies potential impacts on safety, assesses associated risks, and ensures appropriate integration of changes into the SMS.
Developing an effective safety management system requires careful attention to avoid common errors. By addressing leadership commitment, risk assessment, employee involvement, documentation, training, reporting, performance monitoring, communication, continuous improvement, and change management, operators can strengthen their SMS and enhance safety performance. Investing time, resources, and proactive measures in the development and implementation of the SMS will result in a robust safety culture, regulatory compliance, and a safer aviation operation.
###
Read More
Developing a First-Class Safety Policy: Industry Best Practices for FAA Part 5 SMS
July 1, 2024

In compliance with FAA Part 5 Safety Management System (SMS) requirements, developing a comprehensive and effective safety policy is a crucial step for flight organizations. The safety policy sets the foundation for a proactive safety culture and outlines the organization's commitment to safety. In this article, we will explore industry best practices for developing a first-class safety policy as part of an FAA Part 5 SMS, ensuring a robust safety framework and regulatory compliance.
Commitment to Safety at All Levels
A first-class safety policy begins with a clear and unequivocal commitment to safety from top-level management. The policy should reflect the organization's dedication to providing a safe working environment and promoting safe operational practices. Emphasize that safety is a core value and that every employee, from leadership to frontline staff, shares the responsibility for maintaining a high level of safety.
Reflect Regulatory Compliance and Best Practices
Ensure that the safety policy reflects compliance with FAA regulations and industry best practices. Incorporate relevant regulatory requirements into the policy to demonstrate the organization's commitment to meeting and exceeding safety standards. Reference applicable guidelines, standards, and industry-specific requirements that are relevant to the organization's operations.
Define Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of individuals within the organization regarding safety management. Specify the accountabilities of management, safety personnel, and employees at all levels. This clarity helps create a shared understanding of expectations and promotes a culture of accountability for safety performance.
Align with the Organization's Mission and Objectives
Ensure that the safety policy aligns with the organization's overall mission and objectives. Emphasize how safety is an integral part of achieving the organization's goals and how it supports the mission. This alignment helps establish a cohesive approach to safety and reinforces the importance of safety as an organizational priority.
Emphasize Continuous Improvement
Highlight the organization's commitment to continuous improvement in safety performance. Encourage employees to report hazards, near misses, and safety concerns, emphasizing that these reports are opportunities for learning and improvement. Stress the importance of capturing lessons learned and implementing corrective actions to prevent recurrence and enhance safety outcomes.
Provide Clear Reporting and Communication Channels
Establish clear reporting and communication channels for safety-related matters. Encourage open and transparent communication, ensuring that employees feel comfortable reporting safety concerns without fear of retribution. Clearly define the process for reporting incidents, near misses, hazards, and safety suggestions. Provide multiple reporting methods, including anonymous options, to encourage participation.
Training and Competence Development
Highlight the organization's commitment to providing ongoing safety training and competence development. Emphasize the importance of initial and recurrent safety training for all employees. Communicate the organization's investment in resources, such as training programs, workshops, and learning opportunities, to enhance safety knowledge and skills throughout the organization.
Regular Review and Update
Emphasize the importance of regularly reviewing and updating the safety policy. Highlight that the policy is a living document that evolves with changing regulations, industry practices, and organizational needs. Establish a process for periodic review to ensure the policy remains relevant, aligned with best practices, and reflects the organization's evolving safety culture.
Developing a first-class safety policy is a critical step in implementing an FAA Part 5 Safety Management System. By following industry best practices, flight organizations can establish a robust framework that prioritizes safety, complies with regulatory requirements, and fosters a proactive safety culture. A comprehensive safety policy demonstrates the organization's commitment to safety, clearly defines roles and responsibilities, aligns with the organization's mission, emphasizes continuous improvement, provides clear reporting and communication channels, focuses on training and competence development, and undergoes regular review and updates. By implementing these best practices, flight organizations can lay a strong foundation for an effective SMS, ensuring a safe and successful aviation operation.
###
Read More
Attention Part 91 Flight Departments, Repair Stations, Flight Schools, and Drone Operators!
June 10, 2024

The FAA has just opened the Safety Management System Voluntary Program (SMSVP) for a wide range of aviation groups, signaling a serious commitment to enhancing safety standards. Now is the perfect time to enroll in the program, positioning your operation ahead of impending regulations.
Why You Should Take the FAA Seriously and Enroll in the SMSVP Program Now
Regulatory Momentum: The FAA's inclusion of diverse aviation groups in the SMSVP program underscores the swift movement towards mandatory SMS implementation. Enrolling now demonstrates your commitment to safety and stay ahead of the regulatory curve.
Enhanced Safety: The core of the FAA’s SMSVP is to elevate safety standards. By participating in this program, you will systematically identify, analyze, and mitigate risks, significantly reducing the likelihood of accidents and incidents. This proactive approach is essential for safeguarding your operations and personnel.
Operational Readiness: With the FAA's focus on SMS, future regulatory requirements are inevitable. Early adoption of SMS through the SMSVP program ensures that your organization will be fully prepared when these regulations become mandatory, avoiding the scramble to comply at the last minute.
Credibility and Trust: Enrolling in the SMSVP program signals to your clients, partners, and regulatory bodies that your organization prioritizes safety. This enhances your credibility and builds trust, which can lead to more business opportunities and stronger partnerships.
Efficiency and Cost Savings: A well-implemented SMS leads to more efficient operations. By managing safety risks proactively, you can avoid costly disruptions, reduce downtime, and improve overall productivity. The financial benefits of preventing accidents far outweigh the costs of implementing an SMS.
Continuous Improvement: The FAA’s SMSVP emphasizes continuous improvement. Regular evaluations and updates to your safety procedures ensure that your operations remain at the forefront of industry best practices and comply with evolving regulations.
Who Can Enroll?
The FAA SMSVP participation is available to the following 14 CFR parts:
- Part 61 Flight Schools
- Part 91 Living History Flight Experience (LHFE)
- Part 91 Banner Tow
- Part 91 Executive Corporate Operators
- Part 91 subpart K (Part 91K)
- Part 91, 107, and 137 Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS)
- Part 105 Parachute
- Part 125
- Part 133
- Part 137
- Part 141
- Part 142
- Part 145 Repair Stations
- Part 147
Immediate Steps to Take
Enroll in the SMSVP Program: Visit the FAA SMSVP program page to sign up. This is your first step towards establishing a comprehensive safety management system tailored to your operation’s needs.
Develop and Implement Your SMS: Create a robust SMS framework, incorporating safety policies, risk management strategies, and assurance mechanisms. Tailor these components to fit your specific operational context.
Engage Your Team: Success depends on the involvement of everyone in your organization. Conduct thorough training and ensure all team members understand and commit to the SMS processes.
Monitor and Improve: Continuously assess the effectiveness of your SMS. Regular audits and feedback mechanisms are crucial for maintaining high safety standards and adapting to new challenges.
The FAA's decision to open the SMSVP program to such a wide array of aviation groups is a strong indication of their commitment to improving safety across all facets of aviation. Don’t wait until it becomes mandatory—start your SMS journey now and secure the numerous benefits of being an early adopter.
For more information and to enroll, visit the FAA SMSVP program page and take the first step towards a safer, more efficient operation.
###
Read More
Navigating the New FAA Part 5 Rule: Choosing the Right SMS Consultant
May 31, 2024

With the recent release of the new FAA Part 5 rule, there has been a noticeable surge in the number of individuals and companies branding themselves as SMS consultants. While this influx of expertise is great for the aviation industry, it also means that operators need to be extra cautious in selecting a consultant who is truly qualified and capable of guiding them through the complexities of Safety Management Systems (SMS).
The Rise of SMS Consultants
As the FAA's Part 5 SMS requirements come into effect, many operators are seeking assistance to ensure compliance. This demand has led to a proliferation of SMS consultants, some of whom may not have the necessary experience or knowledge to provide the quality of service operators need. It's crucial for operators to thoroughly vet any potential consultants to avoid pitfalls and ensure their SMS is robust and compliant.
Why Vetting Your SMS Consultant is Crucial
An SMS is more than just a set of documents or software; it’s a comprehensive approach to managing safety risks in your operation. Implementing an effective SMS takes time, expertise, and a deep understanding of aviation safety principles. Choosing the wrong consultant can lead to inadequate systems that fail to meet FAA standards, potentially endangering your operation and resulting in non-compliance penalties.
Key Questions to Ask When Vetting an SMS Consultant
What is your experience with SMS implementation?
Ask for specific examples of previous SMS projects they have completed, including the types of operators they have worked with and the outcomes of those projects.
Do you have experience with FAA Part 5 and ICAO Annex 19 SMS requirements?
Ensure the consultant is well-versed in both the FAA Part 5 requirements and international standards set by ICAO Annex 19, as many operators need to comply with both.
Can you provide references from past clients?
Speaking directly with past clients can give you insight into the consultant’s capabilities, work ethic, and effectiveness.
What is your approach to SMS implementation?
Understand their methodology and how they plan to tailor their approach to your specific operation. Avoid one-size-fits-all solutions.
How do you ensure ongoing compliance and continuous improvement?
A good consultant should not only help you achieve initial compliance but also provide strategies for maintaining and improving your SMS over time.
What kind of training and support do you offer?
Effective SMS implementation requires training for your staff. Make sure the consultant offers comprehensive training and ongoing support.
How do you measure the effectiveness of the SMS?
The consultant should have clear metrics and methods for evaluating the performance of your SMS and making necessary adjustments.
What are your fees and what do they cover?
Be clear about the costs involved, including any additional services that might incur extra charges.
As the new FAA Part 5 rule takes effect, the importance of having a well-implemented SMS cannot be overstated. While the rise of SMS consultants offers operators a wealth of options, it also necessitates careful vetting to ensure you choose a consultant who is truly qualified. By asking the right questions and thoroughly evaluating potential consultants, you can find a partner who will help you achieve compliance and enhance the safety of your operations.
Remember, an effective SMS is an investment in the safety and success of your operation. Choose wisely.
###
Read More
Navigating the Timeline: Why Operators Should Act Now on FAA Part 5 SMS Compliance
May 17, 2024

The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has set a challenging timeline for aviation operators: just 36 months to develop and implement a comprehensive Safety Management System (SMS) under the new Part 5 regulations. Given that many organizations typically require 12 to 18 months to fully implement an SMS, this timeline underscores the urgency of beginning the compliance process immediately. Moreover, the complexity of building an SMS from scratch, with no single software or program available to purchase that ensures compliance, adds to the critical need for a strategic, well-planned approach.
Understanding the Timeline Constraints
The 36-Month Challenge
Operators have been given a finite window of 36 calendar months to establish their SMS, a period that may initially seem ample but is tight considering the tasks at hand. These tasks include developing a safety manual, instituting safety policies, training personnel, integrating safety reporting systems, analyzing safety data, and establishing an internal audit program.
Why Quick Implementation Is Crucial
With many organizations needing up to 18 months to fully implement an SMS, those starting late risk incomplete integration by the deadline. Early starters will have the advantage of addressing inevitable challenges—such as integrating new procedures and training staff—without the pressure of imminent deadlines.
The Complexity of SMS Implementation
No Off-the-Shelf Solutions
There is no one-size-fits-all software solution that can fulfill all the requirements of the FAA's Part 5. Operators must develop customized processes that align with their unique operational profiles. This involves:
- Tailoring the safety manual to specific operational needs.
- Developing and refining risk management protocols.
- Training personnel across various roles and responsibilities.
Building from the Ground Up
Creating an SMS is akin to constructing a building: it requires a foundation laid through strategic planning, followed by the construction of individual elements tailored to specific needs and constant evaluation to ensure structural integrity. This process is detailed, iterative, and must be handled with meticulous care.
The Steps to Effective SMS Development
Step 1: Planning and Framework Development
Operators should begin by establishing a clear plan that includes milestones and deadlines. Engaging stakeholders in this early phase is critical to align expectations and responsibilities.
Step 2: Customizing Safety Processes
Since no single software can ensure compliance, operators must develop their safety processes from the ground up. This includes:
- Customized SMS Manual to Organization
- Safety Policy
- Safety Accountabilities and Authorities
- Safety Reporting Program
- SMS Safety Communications
- SMS Record Keeping
- Data Monitoring, Measurement, and Analysis
- Internal Audit Program
- SMS Training
- Emergency Response Plan
- SMS Software (Optional)
Step 3: Integration and Training
Integrating the SMS into daily operations is crucial, and comprehensive training programs should accompany it to ensure that all staff are proficient in their roles within the SMS.
Step 4: Testing and Refinement
Operators need to test the implemented processes under real operational conditions, allowing time to refine and adjust as necessary before the final audit and compliance declaration.
Misconceptions about SMS Software
It is a common misconception among many organizations that purchasing SMS software equates to full implementation. However, this is not the case. While SMS software can significantly aid in the development and management of an SMS by automating data collection, analysis, and reporting, it is not a complete package. Organizations must recognize that software is a tool to facilitate certain aspects of SMS implementation, not a substitute for the comprehensive development and integration of safety practices.
Given the complex requirements and strict timeline set by the FAA, operators must start the SMS development process immediately. The lack of a plug-and-play solution means that each operator must tailor their systems to their specific operational needs, a task that requires time, effort, and strategic foresight. Early action is not just beneficial; it is essential for ensuring compliance, enhancing safety, and ultimately, sustaining operational viability in the competitive and tightly regulated aviation industry.
###
Read More
Preparing for the New FAA Part 5 SMS Mandate: A Guide for Part 135 and Air Tour Operators under 91.147
May 1, 2024

The Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) extension of the Part 5 Safety Management System (SMS) requirements to include Part 135 operators and air tour operators under 91.147 marks a significant evolution in aviation safety standards. This broader inclusion aims to standardize safety management practices across a wider spectrum of the aviation industry. For operators impacted by this change, understanding and preparing for the mandate is crucial. This article provides a targeted guide on how to efficiently prepare for and implement the new FAA Part 5 SMS mandate, ensuring compliance and elevating safety protocols.
Understanding the FAA Part 5 SMS Mandate
The mandate introduces a structured SMS framework that was previously applied primarily to larger commercial airlines under Part 121. Now, Part 135 and 91.147 operators must adopt similar comprehensive safety management practices. This includes establishing systematic processes to manage safety risks, which cover four key components: safety policy, risk management, safety assurance, and safety promotion.
Evaluate Existing Safety Management Systems
Begin by assessing your current safety management practices:
- Review current safety policies and procedures: Determine how well your existing systems align with the new SMS requirements.
- Identify gaps and areas for improvement: Pinpoint where your current safety measures might fall short of the comprehensive SMS standards set forth in Part 5.
Develop or Enhance Your SMS Framework
Based on your initial assessment, develop or refine your SMS to comply fully with the Part 5 standards.
Essential elements to include are:
- Safety Policy: Formalize a safety policy that demonstrates a strong commitment to safety and compliance with FAA requirements.
- Risk Management: Set up procedures to systematically identify, assess, and mitigate risks.
- Safety Assurance: Create mechanisms to continually monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of safety management activities.
- Safety Promotion: Cultivate a robust safety culture through ongoing training and effective communication across all levels of the organization.
Implement Comprehensive Training
Effective SMS implementation requires comprehensive training tailored to your operations:
- Develop specific training modules that cover the key aspects of SMS, tailored to the roles and responsibilities within your operations.
- Ensure continuous education and training to keep all personnel informed about SMS practices and any updates in regulations or internal policies.
Leverage Technology
Utilizing technology can enhance your SMS implementation:
- Adopt SMS software solutions: These can streamline documentation, manage safety reporting, and facilitate monitoring of compliance tasks.
- Employ data analytics: Utilize tools to analyze safety data systematically and identify underlying risk patterns that need addressing.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
SMS is dynamic, requiring ongoing evaluation and refinement:
- Regularly review and assess safety performance using specific metrics and indicators.
- Perform internal audits to ensure compliance and identify areas where your SMS can be improved.
- Encourage open feedback from staff at all levels to continually refine the safety management process.
The extension of Part 5 SMS requirements to Part 135 and 91.147 operators is a proactive step toward enhancing safety across the aviation industry. By thoroughly understanding these requirements, preparing methodically, and engaging your team in these efforts, your operation can not only meet the new regulatory demands but also significantly improve its safety culture. Start planning now to ensure a seamless integration of these vital safety management practices into your daily operations.
###
Read More
Best Questions for Conducting an Internal Audit of a Safety Management System
April 15, 2024

Internal audits play a crucial role in evaluating the effectiveness of a Safety Management System (SMS) within an organization. They help identify areas of non-compliance, potential risks, and opportunities for improvement. Conducting a well-designed internal audit requires asking the right questions to gain valuable insights. In this article, we will explore some of the best questions to include in an internal audit of a safety management system, facilitating a thorough evaluation and enhancement of safety practices.
Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
- Are the organization's safety practices aligned with applicable regulatory requirements and industry standards?
- How does the organization ensure timely updates and compliance with changing regulations?
- Are the necessary permits, licenses, and certifications obtained and maintained as required by regulatory bodies?
Policy and Objectives
- Is the safety policy clearly defined, communicated, and understood by all employees?
- Do the organization's safety objectives align with its overall mission and strategic goals?
- How does the organization ensure that the safety policy and objectives are effectively implemented throughout the organization?
Roles and Responsibilities
- Are the roles and responsibilities related to safety clearly defined at all levels of the organization?
- How are employees held accountable for fulfilling their safety responsibilities?
- Is there a process in place to ensure that employees have the necessary knowledge, skills, and resources to carry out their safety-related tasks?
Hazard Identification and Risk Management
- How does the organization identify and assess hazards specific to its operations?
- Are risk assessments regularly conducted to identify and prioritize potential safety risks?
- How does the organization implement effective controls and mitigation measures to reduce identified risks to an acceptable level?
Reporting and Investigation
- Are there mechanisms in place to encourage employees to report safety concerns, incidents, near misses, and hazards?
- How are safety reports documented, analyzed, and addressed?
- Is there a process for conducting thorough investigations into safety incidents to identify root causes and implement corrective actions?
Safety Communication and Training
- How does the organization ensure effective communication of safety-related information to all employees?
- Are safety briefings, toolbox talks, and safety meetings conducted regularly?
- How does the organization assess training needs and provide necessary safety training to employees?
Safety Performance Monitoring and Measurement
- Are key safety performance indicators (KPIs) established and monitored?
- How does the organization track and report on safety performance trends?
- Are there mechanisms in place to identify areas for improvement and implement corrective actions based on safety performance data?
Continuous Improvement and Lessons Learned
- How does the organization promote a culture of continuous improvement in safety practices?
- Are there processes in place to capture and share lessons learned from safety incidents or near misses?
- How does the organization ensure that corrective actions are effectively implemented and monitored for effectiveness?
Conducting an internal audit of a Safety Management System is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of safety practices within an organization. By including the right questions, organizations can gain valuable insights into compliance with regulatory requirements, policy and objective alignment, roles and responsibilities, hazard identification, risk management, reporting and investigation, safety communication and training, safety performance monitoring, and continuous improvement. These questions serve as a guide to assess the organization's safety practices, identify areas for improvement, and enhance the overall effectiveness of the Safety Management System. Conducting regular internal audits and addressing the findings contribute to a proactive safety culture and ensure a safe and compliant aviation operation.
###
Read More
So You Think You Have an SMS Because You Have a Flight Risk Analysis Tool (FRAT)? Think Again!
April 1, 2024
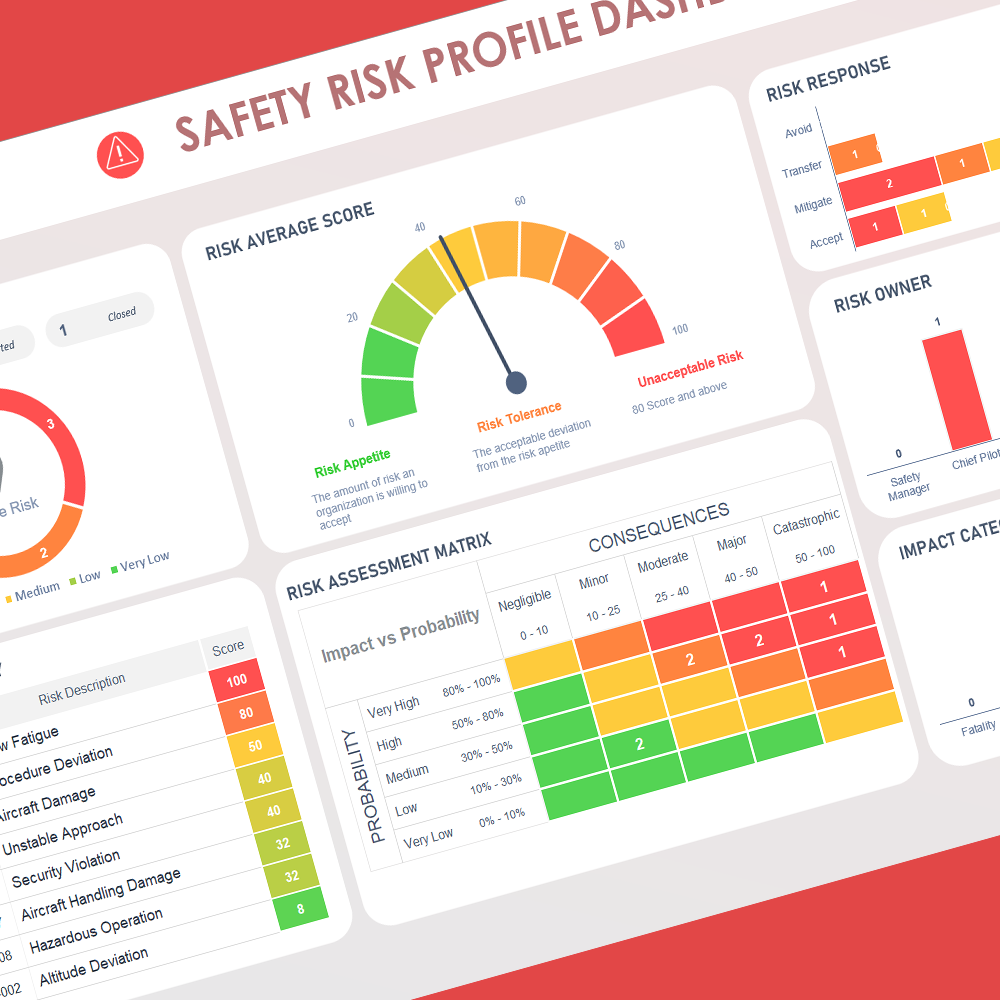
In the realm of aviation safety, confusion often arises between owning a Flight Risk Analysis Tool (FRAT) and having a fully functional Safety Management System (SMS). While a FRAT is a component of an SMS, it’s crucial to understand that having a FRAT alone does not equate to having a comprehensive SMS. A FRAT is not a requirement of a SMS rather it enhances the current system in place. Let’s delve into why this distinction is vital for enhancing safety in aviation operations.
What is a FRAT?
A Flight Risk Analysis Tool is a systematic approach used by flight crews and operators to assess and mitigate risks associated with specific flight operations. By evaluating various factors such as weather conditions, aircraft status, and crew readiness, the FRAT helps in making informed decisions to ensure safety. However, it's a singular element focusing primarily on the pre-flight phase and is limited to assessing and managing the risks of individual flights.
Understanding SMS
On the other hand, a Safety Management System is a much broader and more integrated approach to managing safety, including policy, objectives, plans, procedures, organization, responsibilities, and other measures. An SMS encompasses all aspects of safety risk management, safety assurance, safety promotion, and safety policy. It’s an organizational framework that systematically addresses safety through various components and processes, ensuring that safety management becomes an integral part of the organization’s culture and operations.
Why FRAT is Not Enough
- Scope of Operations: While a FRAT provides a snapshot of risk for a specific flight, an SMS offers a holistic view of the entire operational safety. SMS involves continuous monitoring and analysis of all operations, not just flight-specific risks.
- Continuous Improvement: SMS is based on the principle of continuous improvement. It involves regular monitoring, evaluation, and improvement of safety processes, whereas a FRAT is a one-time risk assessment tool for individual flights.
- Organizational Culture: SMS fosters a safety culture within the organization, encouraging open communication and reporting of safety issues without fear of retribution. A FRAT alone cannot cultivate such a culture; it requires the supportive framework of an SMS.
- Compliance and Integration: Regulatory bodies like the FAA and ICAO require operators to implement an SMS, recognizing it as a comprehensive approach to managing safety. A FRAT is just one of the many tools integrated into this system.
- Proactive and Reactive Measures: SMS not only looks at proactive measures to prevent accidents and incidents but also includes reactive processes for learning and evolving from them. FRAT primarily focuses on proactive risk assessment.
While a Flight Risk Analysis Tool is an important element in identifying and mitigating flight-related risks, it’s just the tip of the iceberg in the realm of safety management. A robust SMS is an integrated, organization-wide approach that encompasses much more than just risk assessment. It ensures a systemic and procedural approach to managing safety, with the ultimate goal of fostering a pervasive culture of safety within the organization. So, if you think you have an SMS just because you have a FRAT, it’s time to reevaluate and consider the broader, more comprehensive approach needed to truly ensure safety in aviation operations.
###
Read More
Enhancing Safety on Board: The Imperative of Emergency Procedures Training for Executives and Passengers on Business Jets
March 15, 2024

In the world of private aviation, where the luxury of personalized travel meets the efficiency of direct routes, the paramount importance of safety can never be overstated. Business jet travel offers a unique set of advantages, but it also requires a specific focus on emergency preparedness, particularly in the absence of a flight attendant. Recent tragic incidents within our industry underscore the critical need for executives and passengers to be well-versed in emergency procedures, ensuring the highest level of safety and readiness in unforeseen situations.
The Case for Comprehensive Emergency Training
While business jet aircraft are designed with safety as a cornerstone, the reality of aviation is that emergencies, though rare, can occur. The absence of a flight attendant on many charter and business jet flights places the onus of initial emergency response on the passengers themselves. In such scenarios, familiarity with the aircraft's emergency equipment and procedures is not just beneficial—it could be life-saving.

Key Areas of Emergency Procedures Training
- Opening Emergency Exits and Doors: Passengers should be instructed on how to operate emergency exits and doors. This includes understanding the mechanisms involved and the physical requirements to effectively open them under various conditions.
- Access to First Aid and AED Equipment: Knowing the location and proper use of first aid supplies and Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) is vital. Quick access and efficient use of these tools can make a significant difference in medical emergencies.
- Utilization of Fire Extinguishers: Fires on aircraft present a severe risk. Training on the types of fire extinguishers available on board, their locations, and the fundamentals of their operation is essential for passenger safety.
- Life Vests and Life Rafts Deployment: Over-water flights necessitate a clear understanding of how to use life vests and deploy life rafts. Passengers should be familiar with where these items are stored and the steps required to use them effectively.
- Familiarity with Other Emergency or First Aid Equipment: Depending on the aircraft, additional safety equipment may be available. Passengers should be briefed on all such items before takeoff.

Implementing Effective Training Programs
Effective emergency procedures training for passengers begins with a comprehensive pre-flight safety briefing. These briefings should be more than just a formality; they need to engage and educate passengers on the critical aspects of emergency preparedness. Interactive sessions that allow for hands-on practice with safety equipment can significantly enhance passengers' confidence and competence in handling potential emergencies.
For operators and charter companies, incorporating detailed safety cards, instructional videos, and even virtual reality simulations can further reinforce this vital information. Tailoring the content to the specific configurations of each aircraft ensures that passengers receive relevant and actionable guidance.
The Importance of Regular Review and Practice
Safety is a dynamic field, requiring ongoing education and practice. Regular review sessions for frequent flyers, along with updates on any new safety equipment or procedures, ensure that passengers' knowledge remains current. Encouraging questions and providing clear, concise answers helps to demystify the emergency equipment and procedures, making passengers more likely to remember and correctly perform these actions if needed.
In light of recent events, the importance of thorough emergency procedures training has never been clearer. As we continue to advance in our pursuit of aviation excellence, let us not overlook the fundamental aspect of safety training for all onboard. By empowering passengers with the knowledge and skills to act decisively during emergencies, we honor the legacy of those we've lost and reaffirm our commitment to the highest safety standards in private aviation.
###
Read More
The Strategic Advantage of Audits in Crisis: Strengthening Safety When It Matters Most
February 29, 2024

In the dynamic world of operations, where unpredictability is the only constant, the notion of conducting an audit amidst a crisis might seem counterintuitive, if not outright daunting, to many. The idea of scrutinizing processes, practices, and performances while in the throes of operational challenges can be overwhelming. Yet, it is precisely in these moments, when teams are navigating their lowest points and engagement levels have dipped due to emerging risks, that the true value of an audit becomes unmistakably clear.
The Unseen Opportunity Amidst Crisis
The concept that in the middle of the battle is the best time to audit may appear unconventional at first glance. Traditionally, audits are often viewed as post-mortem exercises conducted in the calm after the storm to assess what went wrong. However, this perspective overlooks the transformative potential of audits as proactive tools for strengthening safety and performance in real-time.
When a team faces significant hurdles, and engagement levels are waning under the pressure of compounded risks, an audit can serve as a critical intervention. It offers a structured opportunity to re-evaluate and adjust safety measures, ensuring that they are not just theoretically robust but practically resilient.
The Resistance to Mid-Crisis Audits
Many operators resist the idea of mid-crisis audits due to concerns about additional stress on an already burdened team or fears that it might expose more flaws, further complicating the situation. This resistance is understandable; after all, focusing on immediate operational recovery seems instinctual. However, avoiding audits during these periods misses a crucial point: crises expose vulnerabilities in safety systems that might remain hidden during smoother operations.
The Case for Auditing During Downfalls
Auditing in the midst of a crisis does more than just identify weaknesses; it fosters a culture of transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement. It encourages teams to rally together, critically assess their current state, and demonstrate their commitment to safety in the face of adversity. This process not only addresses immediate risks but also strengthens the team's resilience against future challenges.
Moreover, audits conducted during low points provide invaluable insights into the real-world effectiveness of safety protocols under stress. They allow organizations to make informed adjustments that are directly responsive to the current operational context, rather than theoretical scenarios.
Turning Challenges into Opportunities
The most critical advantage of conducting an audit during challenging times is the opportunity it presents for immediate corrective action. It enables teams to pivot quickly, applying lessons learned in real-time to mitigate ongoing risks. This proactive approach can transform a period of vulnerability into a strategic advantage, enhancing safety outcomes and operational efficiency.
The reluctance to engage in audits during operational crises is natural, but rethinking this stance can unlock significant benefits. Mid-crisis audits are not just about accountability; they're about opportunity—the chance to turn adversity into strength, to rally as a team, and to demonstrate an unwavering commitment to safety even in the toughest times. By embracing audits as essential tools for navigating crises, organizations can foster a culture of resilience that stands strong in the face of any challenge.
###
Read More
Fostering a Culture of Safety: Promoting a Safety Management System in a Small Flight Department
February 12, 2024

Safety management systems (SMS) are vital for promoting a proactive and systematic approach to safety within aviation organizations. While larger flight departments may have more resources and dedicated safety personnel, smaller flight departments face unique challenges when it comes to promoting and implementing a robust SMS. In this article, we will explore effective strategies to promote a safety management system in a small flight department, fostering a culture of safety and enhancing operational excellence.
Leadership Commitment
Promoting a safety management system starts with strong leadership commitment. The leaders of the flight department must demonstrate a genuine commitment to safety and lead by example. Establish safety as a core value, prioritize it in decision-making processes, and allocate necessary resources to support the SMS implementation and continuous improvement.
Communication and Engagement
Effective communication is crucial to promote the importance of the SMS throughout the flight department. Clearly communicate the objectives and benefits of the SMS to all employees, emphasizing their roles and responsibilities in maintaining a safe operation. Encourage open dialogue and active participation, welcoming suggestions, feedback, and safety-related concerns from all members of the department.
Training and Education
Invest in training and education programs to ensure that all employees have the knowledge and skills required to support the SMS. Provide comprehensive initial and recurrent training on safety policies, procedures, and risk management practices. Tailor the training to the specific needs and operations of the flight department, promoting a deep understanding of the SMS and its relevance to daily tasks.
Safety Reporting and Confidentiality
Create a reporting culture that encourages employees to report safety concerns, incidents, near misses, or hazards without fear of reprisal. Establish a confidential reporting system that protects the anonymity of individuals, allowing them to share information openly and without hesitation. Encourage the reporting of both positive safety performance and areas for improvement, emphasizing the importance of learning from past experiences.
Safety Risk Management
Implement a structured safety risk management process within the flight department. Encourage employees to identify hazards, assess risks, and propose mitigation strategies. Foster a proactive approach to risk management by conducting regular risk assessments, evaluating safety trends, and implementing appropriate controls to minimize risks. Communicate the outcomes of risk assessments and demonstrate the effectiveness of risk mitigation measures.
Continuous Improvement
Promote a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reviewing the SMS and identifying opportunities for enhancement. Conduct internal audits to evaluate the effectiveness of safety procedures, documentation, and compliance with regulations. Engage employees in identifying areas for improvement and encourage their active participation in the development of corrective actions and safety initiatives.
Recognition and Incentives
Acknowledge and recognize individuals and teams that demonstrate exceptional commitment to safety. Establish safety-related incentives or rewards programs to encourage active participation, engagement, and adherence to safety protocols. Celebrate safety milestones, achievements, and successful safety initiatives to reinforce the importance of safety within the flight department.
Promoting a safety management system in a small flight department requires dedicated efforts, strong leadership, and a commitment to fostering a culture of safety. By emphasizing leadership commitment, effective communication, comprehensive training, safety reporting, risk management, continuous improvement, and recognition, flight departments can successfully promote and integrate an SMS. Through these strategies, small flight departments can enhance safety awareness, mitigate risks, and create a safe and resilient operating environment, ensuring the well-being of their employees and the success of their operations.
###
Read More
Closing Out 2023: A Year of Milestones and Growth at Aviation Safety Solutions
January 28, 2024

As we close the chapter on 2023, it's a perfect moment to reflect on the journey of Aviation Safety Solutions, a name synonymous with excellence and safety. From our humble beginnings to becoming a leader in the industry, it's been a remarkable journey fueled by passion and expertise.
Our Humble Beginnings: The Vision of Amanda Ferraro
Our story began a decade ago when Amanda Ferraro, driven by her passion for aviation safety, became an auditor in 2013. With a clear vision and dedication, Aviation Safety Solutions was born. Initially, our focus was on safety auditing, a crucial aspect of aviation that ensures the highest standards are met.
Growth and Diversification: Beyond Auditing to a Spectrum of Services
From that single-employee start-up, we have grown exponentially. Today, we proudly have over 32 employees, including 15 IS-BAO auditors, each bringing a wealth of knowledge and experience to our team. We’ve expanded from being solely an auditing firm to offering consulting and training services, encompassing every aspect of safety, industry best practices, and standards. Our services have transcended the fixed and rotary wing aircraft space. Our team has had the honor and opportunity to work in safety technologies, bridging crucial gaps for innovation and innovative products in the broader transportation space.
Innovative Training: Launch of the IS-BAO Standardization Protocol Course
2023 marked the launch of the IS-BAO Standardization Protocol Course, a groundbreaking initiative in collaboration with IBAC. This course answers the longstanding industry question: "What do these standards mean, and how do I apply them to my operation?" It is an online, animated training program, providing clarity for each standard within the IS-BAO program. This course represents our commitment to demystifying and disseminating crucial safety standards for the benefit of the industry.
From Safety Assistance to Training Academy
A significant milestone was the introduction of our Safety Assistance Program in 2018. This program helped operators develop robust safety management systems and achieve their personalized safety goals. In 2023, our safety assistance clients achieved numerous milestones, including enrollment in and compliance with the FAA SMSVP program, becoming registered IS-BAO operators, preparing for Wyvern and ARGUS audits, and obtaining EASA/UK TCO approvals.
The launch of our new branding and website in 2023 marked a new era for Aviation Safety Solutions. Our Training Academy is a testament to our commitment to continuous improvement and client empowerment, offering internal audit checklists, various courses, emergency response training programs, and online emergency response exercise.
FAA SMS Workshop: The Highlight of 2023
A highlight of 2023 was the introduction of the FAA SMS Workshop in collaboration with Fireside Partners, our industry's premier emergency response experts. This workshop represents a significant step forward in our ongoing mission to elevate aviation safety standards and practices.
Looking Forward: The Sky is the Limit
As we bid farewell to 2023, we at Aviation Safety Solutions are filled with gratitude and excitement. Gratitude for the trust that our clients place in us, and excitement for the future. Our journey from a small auditing firm to a leading provider in safety management systems and beyond is a story of passion, perseverance, and constant evolution.
In closing, we look forward to 2024 with optimism and the unwavering commitment to enhancing aviation safety and beyond. The sky is not the limit; it's our playground. Thank you for being part of our journey. Here's to soaring even higher in the coming years!
Aviation Safety Solutions Team
###
Read More
Connecting SMS for the Future
December 15, 2023
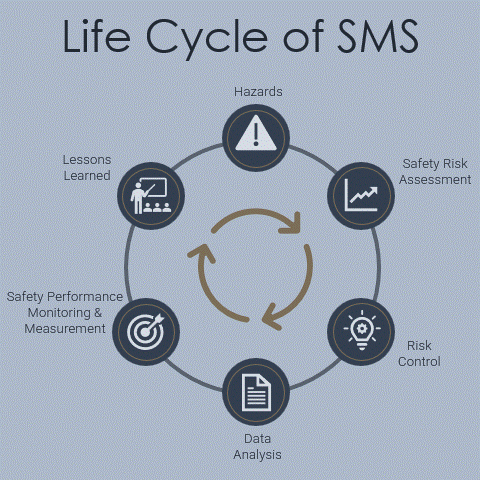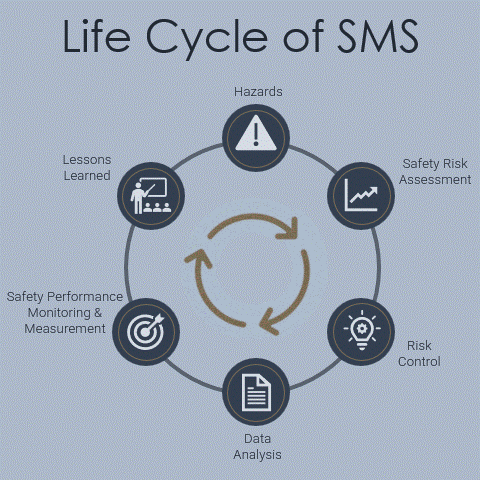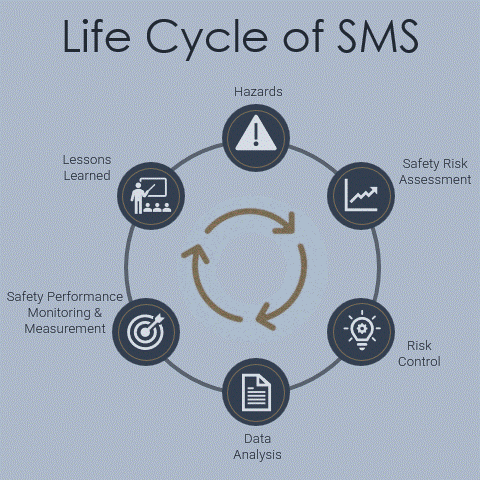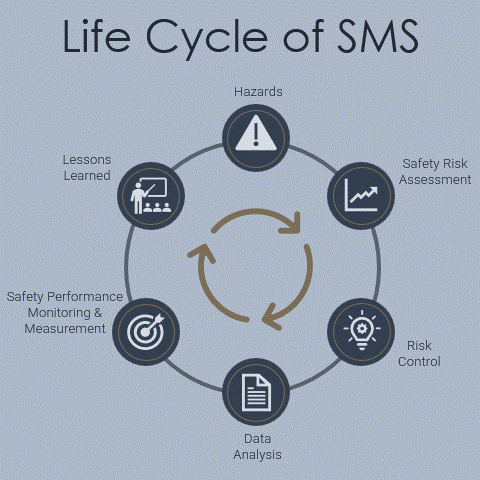
As of the current state, safety management systems (SMS) have become an integral part of aviation and various other industries. They serve as a structured approach to managing safety, encompassing policies, procedures, and practices that aim to proactively identify and mitigate risks. The implementation of SMS has significantly improved safety standards, reducing the number of accidents and incidents across industries.
However, the current state of safety management systems faces some challenges. One of the key issues is the lack of integration and connectivity among various safety-related processes and systems within an organization. Many companies have separate systems for incident reporting, risk assessments, safety training, and compliance monitoring, leading to fragmented safety data and disjointed safety efforts.
To enhance the effectiveness of safety management systems, they need to become connected and holistic. Why is this shift crucial?
Comprehensive Risk Management
A connected SMS allows organizations to identify and assess risks more comprehensively by analyzing data from multiple sources. This integrated approach provides a more accurate understanding of potential hazards and enables proactive risk management.
Real-time Monitoring
With a holistic SMS, safety-related data can be monitored in real-time. This real-time monitoring enables faster identification of safety trends and emerging risks, allowing organizations to take swift corrective actions.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Connected safety management systems facilitate data-driven decision-making. Organizations can use analytics and insights from various safety processes to make informed decisions and allocate resources more effectively.
Streamlined Reporting and Compliance
Integrating safety processes streamlines reporting and compliance requirements. A connected SMS reduces duplicate efforts, minimizes administrative burden, and ensures accurate and timely reporting.
Cultivating a Safety Culture
A holistic SMS promotes a strong safety culture throughout the organization. When safety efforts are interconnected and visible, it reinforces the importance of safety at all levels, leading to increased engagement and commitment to safety principles.
Enhanced Collaboration
Connecting safety management systems encourages collaboration among different departments and stakeholders. This collaboration fosters the sharing of best practices and lessons learned, leading to continuous improvement in safety performance.
Proactive Hazard Identification
A connected SMS facilitates the identification of hazards at an early stage. This early detection enables organizations to implement preventive measures, reducing the likelihood of incidents and accidents.
The current state of safety management systems has undoubtedly improved safety standards across various industries. However, to take safety to the next level, SMS needs to become connected and holistic. Integration and connectivity among safety processes enable comprehensive risk management, real-time monitoring, data-driven decision-making, streamlined reporting, and a strong safety culture. By embracing a more interconnected approach to safety management, organizations can effectively enhance safety performance and create safer working environments for their employees and stakeholders.
###
Read More
Making the Case: Convincing Executive Leadership of the Value of an SMS for Small Flight Departments
December 1, 2023

Implementing a Safety Management System (SMS) is a critical investment for small flight departments to enhance safety, improve operational efficiency, and ensure regulatory compliance. However, persuading executive leadership to allocate financial resources for an SMS can be a challenge. In this article, we will explore effective strategies to demonstrate the value and worthiness of an SMS for small flight departments, helping you make a compelling case to executive leadership.
Highlight Safety Benefits - The primary goal of an SMS is to enhance safety within the organization. Emphasize the potential reduction in accidents, incidents, and associated costs that an SMS can bring. Present statistics and case studies showcasing how SMS implementation has resulted in improved safety performance for similar organizations. Stress the importance of protecting the well-being of employees, passengers, and the organization's reputation.
Emphasize Regulatory Compliance - An SMS is not just a recommendation but a regulatory requirement in many jurisdictions. Highlight the consequences of non-compliance, including potential fines, penalties, and reputational damage. Demonstrate that implementing an SMS proactively ensures compliance with aviation regulations, mitigates legal risks, and positions the flight department as a responsible and reputable operator.
Cost-Benefit Analysis - Conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis to demonstrate the financial advantages of implementing an SMS. Consider the potential savings in insurance premiums, reduced maintenance costs due to improved safety practices, and lower expenses associated with accidents or incidents. Additionally, highlight the long-term cost-effectiveness of preventing safety-related disruptions to operations and potential legal liabilities.
Operational Efficiency and Risk Management - An SMS streamlines operational processes, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings. Showcase how the SMS helps identify and manage risks, leading to optimized decision-making and resource allocation. Explain how risk assessments and safety data analysis enable the flight department to proactively address safety concerns and allocate resources effectively, resulting in a more efficient and profitable operation.
Industry Best Practices and Reputation - Implementing an SMS aligns the flight department with industry best practices and demonstrates a commitment to safety excellence. Highlight that an SMS enhances the flight department's reputation among customers, business partners, and industry stakeholders. Emphasize that investing in an SMS positions the organization as a preferred choice for clients who prioritize safety and provides a competitive advantage in the aviation industry.
Employee Engagement and Retention - An SMS promotes a safety culture and engages employees in safety-related activities. Emphasize the positive impact on employee morale, job satisfaction, and retention rates. Explain that investing in an SMS shows the organization's commitment to employee well-being, fostering a positive work environment and increasing loyalty among staff members.
Continuous Improvement and Future Preparedness - An SMS facilitates a continuous improvement mindset, allowing the flight department to adapt to changing industry trends and regulations. Stress the importance of future-proofing the organization by implementing an SMS that can evolve with the aviation industry. Demonstrate how an SMS provides a framework for ongoing safety enhancements, adaptability to new technologies, and the ability to meet evolving customer expectations.
Persuading executive leadership of the value of an SMS for a small flight department requires a strategic approach. By highlighting safety benefits, regulatory compliance, cost-effectiveness, operational efficiency, industry reputation, employee engagement, and future preparedness, you can make a compelling case. Effectively communicate the advantages an SMS brings to the organization's safety performance, operational excellence, regulatory compliance, and long-term sustainability. With a well-crafted argument that addresses the specific needs and concerns of the flight department, you can secure executive support and the necessary financial resources to implement an SMS, ensuring a safer and more successful aviation operation.
###
Read More
Unlocking Excellence: How Flight Operators Benefit from the IS-BAO Standardization Protocol Course
November 14, 2023

In the aviation industry, safety and operational efficiency are paramount. To achieve and maintain the highest standards, flight operators are increasingly turning to the International Standard for Business Aircraft Operations (IS-BAO). As a crucial component of IS-BAO implementation, the IS-BAO Standardization Protocol Course empowers flight operators, both those who have already implemented IS-BAO and new entrants, with valuable knowledge and tools. In this article, we explore the benefits that flight operators can derive from undertaking the IS-BAO Standardization Protocol Course.
Flight Operators with Existing IS-BAO Implementation
For flight operators who have already implemented IS-BAO, the Standardization Protocol Course offers several advantages.
Strengthened Safety Culture - The course enhances safety awareness and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. It equips operators with the latest best practices and ensures that their safety management systems (SMS) remain up-to-date.
Compliance and Auditing Excellence - The course provides operators with comprehensive knowledge of IS-BAO standards, facilitating ongoing compliance and audit preparation. It enables operators to consistently meet regulatory requirements and effortlessly navigate audits.
Efficiency and Operational Excellence - By fine-tuning SMS processes, the course helps operators identify areas for improvement, streamline operations, and enhance overall efficiency. This results in optimized resource allocation, reduced costs, and improved performance metrics.
Industry Recognition and Competitive Edge - Completion of the Standardization Protocol Course demonstrates a commitment to excellence and compliance with internationally recognized standards. This enhances an operator's reputation, instills confidence in stakeholders, and provides a competitive advantage in the market.
New Entrant Flight Operators
For flight operators who are new to IS-BAO and considering its implementation, the Standardization Protocol Course offers invaluable benefits.
In-Depth Understanding - The course provides a comprehensive understanding of IS-BAO principles, requirements, and implementation processes. It equips new operators with the knowledge necessary to establish and maintain a robust SMS from the outset.
Efficient Implementation - By following the course's guidelines, new entrant operators can avoid common pitfalls and streamline the implementation of IS-BAO. This saves time, resources, and minimizes potential disruptions during the integration process.
Immediate Compliance - The Standardization Protocol Course ensures that new entrant operators are well-versed in regulatory requirements, facilitating compliance right from the start. This establishes a solid foundation for safety and regulatory excellence.
Networking and Collaboration - The course provides an opportunity for new operators to network with industry professionals, share experiences, and learn from established operators who have successfully implemented IS-BAO. This fosters collaboration and creates a supportive community.
The IS-BAO Standardization Protocol Course is a powerful resource that empowers flight operators, both those with existing IS-BAO implementation and new entrants, to achieve excellence in safety management and operational efficiency. For operators already utilizing IS-BAO, the course ensures continuous improvement, compliance, and enhanced safety culture. New entrants benefit from the course by gaining a comprehensive understanding of IS-BAO, efficient implementation processes, immediate compliance, and access to industry networks.
Embracing the IS-BAO Standardization Protocol Course sets flight operators on a path to excellence, regulatory compliance, and industry recognition. By investing in this comprehensive training, operators propel their organizations forward, fostering a safer, more efficient, and prosperous future for the aviation industry as a whole.
###
For more information on the IS-BAO Standardization Protocol Course please visit our Training Academy website.
Read More
Implementing FAA Part 5 SMS When Already Compliant with ICAO Annex 19 SMS
November 1, 2023

For aviation operators that already comply with the International Civil Aviation Organization's (ICAO) Annex 19 Safety Management System (SMS), implementing the Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) Part 5 SMS requirements may seem like a challenging endeavor. However, by leveraging existing SMS practices and addressing specific FAA requirements, organizations can successfully integrate the two frameworks. This article outlines the key steps to implement FAA Part 5 SMS while building upon an established compliance with ICAO Annex 19 SMS.
Conduct a Gap Analysis
Begin by conducting a comprehensive gap analysis comparing the existing SMS practices aligned with ICAO Annex 19 against the specific requirements outlined in FAA Part 5. This analysis will identify areas where additional processes, procedures, or documentation may be needed to meet the FAA's regulatory expectations.
Customize SMS Processes
While ICAO Annex 19 provides a solid foundation, it is essential to customize SMS processes to align with the specific requirements of FAA Part 5. This may involve developing or modifying certain procedures, manuals, or documentation to meet the FAA's unique expectations and regulatory structure.
Update Documentation and Procedures
Review and update existing SMS documentation, including safety policies, manuals, procedures, and forms, to ensure they comply with both ICAO Annex 19 and FAA Part 5 requirements. Consider any additional elements or modifications necessary to satisfy FAA-specific regulations.
Training and Education
Provide training and education to employees to ensure they are familiar with the FAA Part 5 SMS requirements. Highlight any differences between the two frameworks and emphasize the importance of adhering to both sets of standards. Training should encompass roles and responsibilities, hazard identification, risk management, and reporting procedures specific to the FAA's requirements.
Operational Integration
Integrate the FAA Part 5 SMS requirements into the day-to-day operations of the organization. Ensure that safety processes and practices are aligned with both ICAO Annex 19 and FAA Part 5. Foster a culture that embraces the objectives of both frameworks, encouraging proactive hazard reporting, risk assessment, and continuous improvement.
Safety Performance Monitoring and Evaluation
Establish a robust safety performance monitoring and evaluation system that encompasses both ICAO Annex 19 and FAA Part 5 requirements. Implement key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics that align with the goals of both frameworks. Regularly review safety data, conduct internal audits, and analyze trends to identify areas for improvement and track progress towards meeting both ICAO and FAA standards.
Engagement with Regulatory Authorities
Engage with regulatory authorities, both at the national level (FAA) and within other jurisdictions where the organization operates, to ensure compliance and seek guidance on any unique requirements or interpretations of the regulations. Foster open communication channels to stay informed about regulatory updates and changes that may impact SMS implementation.
Integrating FAA Part 5 SMS requirements into an existing ICAO Annex 19 SMS framework requires a systematic approach and a commitment to compliance. By conducting a gap analysis, customizing SMS processes, updating documentation and procedures, providing training, integrating operations, monitoring safety performance, and engaging with regulatory authorities, aviation operators can successfully implement FAA Part 5 SMS while building upon their existing compliance with ICAO Annex 19. This integrated approach will enhance safety management practices, promote regulatory compliance, and ultimately contribute to a safer and more efficient aviation operation.
###
Read More
From Tragedy to Triumph: Amanda Ferraro's Journey to Aviation Safety
October 14, 2023

In the world of aviation safety, Amanda Ferraro stands out not just as a CEO but as a remarkable individual whose passion for safety was born out of a life-altering event. Her journey from a tragic accident at the age of 17 to founding Aviation Safety Solutions is a testament to her unwavering commitment to making aviation safer for all.
A Fateful Fall
Amanda's story begins with a fall, a fall that would change her life in more ways than one. At 17 years old, she embarked on a ropes course adventure, not knowing that it would lead to a traumatic accident. She fell a harrowing 30 feet, headfirst, and the impact was devastating. The brunt of the fall was taken by her arms, shattering her right elbow and both wrists.
The road to recovery was anything but easy. Amanda underwent six major reconstructive surgeries, each one a grueling battle to rebuild her shattered limbs. But her determination and resilience were unwavering. She didn't just recover; she emerged stronger, with a newfound appreciation for the importance of safety and the precious gift of life itself.
Learning to Write Again
One of the most profound challenges Amanda faced during her recovery was learning how to write again. The injuries to her arms had been so severe that even the simplest tasks, like picking up a pen, seemed insurmountable. But Amanda's spirit refused to be broken. She painstakingly relearned the art of writing, a symbolic act of triumph over adversity.
A Passion for Aviation Safety
Amanda's journey to recovery didn't just rebuild her body; it ignited a passion for aviation safety. She recognized that safety wasn't just a set of rules and regulations; it was a deeply personal commitment to protecting lives. Her own experience taught her that safety is more than a profession; it's a calling.
This profound realization led Amanda to found Aviation Safety Solutions, a company dedicated to pushing the boundaries of safety in the aviation industry. Her unique perspective, born from personal hardship, fuels her unwavering commitment to making aviation safer for everyone who takes to the skies.
Why Aviation Safety Solutions is Different
What sets Aviation Safety Solutions apart is Amanda Ferraro's personal journey. Her tragic accident and the challenges she overcame to regain her life and independence provide a unique perspective on the importance of safety. It's a perspective that drives her company to go above and beyond in ensuring the highest standards of safety in aviation.
Amanda's story is a powerful reminder that safety isn't just a job; it's a personal mission. It's about understanding the human cost of accidents and the lives that can be forever changed. Through her dedication and the work of Aviation Safety Solutions, she is making aviation safer, one step at a time.
In every aspect of her life and work, Amanda Ferraro exemplifies the spirit of resilience and the unyielding commitment to safety. Her journey is an inspiration, and her company is a testament to the transformative power of passion and purpose.
###
Read More
Safety Manager as a Mentor: Empowering SMS in Aviation
October 1, 2023
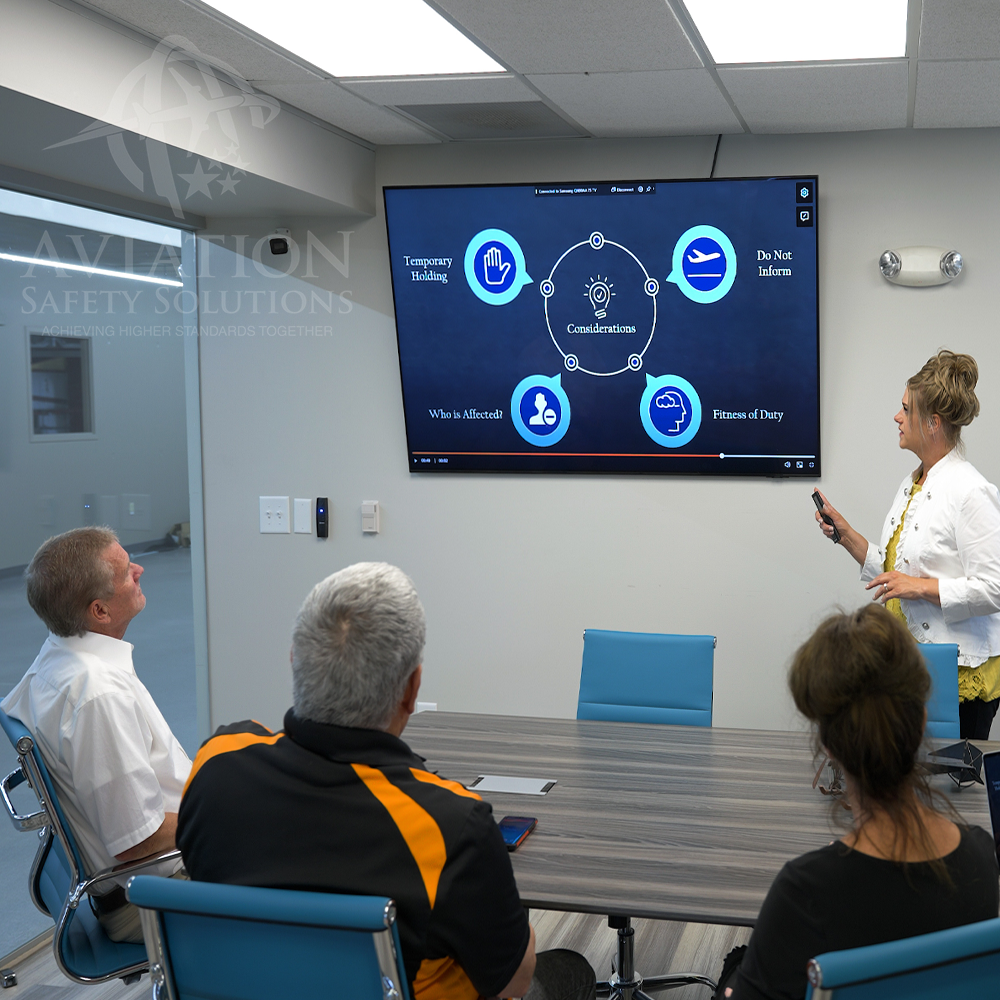

In the dynamic world of aviation safety, the role of a Safety Manager has traditionally been multifaceted, often encompassing the entire Safety Management System (SMS). However, it's time for a paradigm shift. Safety Managers should evolve into facilitators and mentors, guiding organizations to take ownership of their safety processes.
The Traditional Safety Manager
Historically, the Safety Manager held the reins of the SMS, overseeing risk assessments, safety procedures, and incident reporting. This approach centralized safety within the role, creating a bottleneck that hindered organizational growth and innovation.
The New Paradigm - Safety Manager as Mentor
Picture a Safety Manager not as the SMS itself, but as a mentor who empowers the entire organization to embrace safety as a shared responsibility. Here's how this transformation can benefit the aviation industry:
Fostering a Culture of Safety: Safety should be embedded in the DNA of every aviation professional. A mentorship-based approach cultivates a culture where every team member understands their role in safety and actively contributes.
Encouraging Proactive Risk Management: Safety Managers as mentors inspire managers and staff to conduct their risk assessments. This decentralization of responsibility ensures that safety is not just a bureaucratic process but an ongoing commitment.
Promoting Continuous Improvement: Safety is not a static concept. It's a dynamic process that demands constant evaluation and refinement. Safety Managers, in their mentoring role, guide organizations in monitoring and improving safety measures over time.
Nurturing Leadership Skills: Safety Managers should mentor leaders within the organization to be safety advocates. This enables a top-down approach where safety is championed at every level.
Expanding Expertise: As mentors, Safety Managers provide the knowledge and tools needed for personnel to make informed safety decisions independently.
The Path Forward
Transforming the role of a Safety Manager from a centralized figure to a mentor requires a cultural shift within the aviation industry. Organizations must recognize the value of decentralized safety and commit to investing in mentorship and training programs.
In aviation safety, the future is bright when Safety Managers become mentors who inspire, educate, and empower their teams. By shifting from a singularly responsible role to one of guidance and support, the industry can create a safer, more resilient environment where everyone plays an active role in mitigating risks and ensuring safe skies. This evolution represents not only a change in job description but a fundamental transformation in the way we approach aviation safety.
###
Read More
Crafting a Comprehensive Emergency Response Exercise Scenario for Business Aviation Operators
September 18, 2023

Emergency response exercises play a crucial role in preparing business aviation operators to effectively respond to potential crises. Developing a thorough exercise scenario is essential to simulate realistic and challenging situations that test the organization's emergency response capabilities. In this article, we will outline key steps to help business aviation operators create a comprehensive emergency response exercise scenario that aligns with their specific operational context.
Identify Relevant Hazards and Risks
Begin by conducting a thorough risk assessment to identify the potential hazards and risks specific to your business aviation operation. Consider factors such as aircraft accidents, security threats, natural disasters, medical emergencies, and operational disruptions. Analyze historical data, regulatory requirements, and industry best practices to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the risks faced.
Define Exercise Objectives and Scope
Clearly define the objectives and scope of the exercise. Determine what specific skills, procedures, or systems you want to evaluate and improve. Consider the exercise's timeframe, location, and the number of participants involved. Align the exercise objectives with your organization's emergency response plans, regulatory requirements, and operational priorities.
Develop a Realistic Scenario
Craft a realistic and engaging scenario that challenges participants and simulates a crisis situation. Consider the identified hazards and risks, the location of the exercise, and the capabilities of your organization. Create a narrative that encompasses the incident, its cause, the potential consequences, and any relevant factors such as weather conditions, time of day, or available resources. The scenario should realistically test the organization's emergency response procedures and decision-making processes.
Incorporate Interactive Elements
Make the exercise scenario interactive by including elements that require participants to make decisions and take actions. Introduce unexpected developments, changing circumstances, and information gaps to keep participants engaged and simulate the dynamic nature of real emergencies. Interactive elements could include simulated communications, role-playing, time pressure, or resource limitations.
Involve Stakeholders
Engage key stakeholders in the exercise scenario to enhance realism and coordination. Collaborate with airport authorities, air traffic control, emergency services, regulatory agencies, and other relevant entities. Ensure that each stakeholder understands their role within the scenario and their specific objectives. Encourage active participation and coordination among stakeholders to simulate the collaborative nature of emergency response in a real-world setting.
Incorporate Evaluation Mechanisms
Develop a robust evaluation plan to objectively assess the performance of participants during the exercise. Define clear evaluation criteria, performance indicators, and benchmarks. Assign experienced evaluators who can observe and assess participants' actions, decisions, and communication. Consider utilizing evaluation forms, debriefing sessions, and post-exercise surveys to gather feedback and capture lessons learned.
Analyze Lessons Learned and Implement Improvements
After the exercise, conduct a thorough analysis of the lessons learned. Review feedback, observations, and evaluation results to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. Use this information to update emergency response plans, procedures, and training programs. Implement corrective actions and communicate the findings to relevant stakeholders to drive continuous improvement in the organization's emergency response capabilities.
Developing a thorough emergency response exercise scenario is a critical step for business aviation operators to enhance their preparedness and response capabilities. By identifying hazards and risks, defining exercise objectives, creating realistic scenarios, incorporating interactive elements, involving stakeholders, implementing evaluation mechanisms, and analyzing lessons learned, operators can simulate realistic crises and effectively test their emergency response systems. Through regular exercises and continuous improvement efforts, business aviation operators can ensure a state of readiness and resilience, prioritizing safety and maintaining the highest standards of emergency response in their operations.
###
Read More
Assessing Safety Culture in Small Flight Departments: Key Questions for a Safety Culture Survey
September 1, 2023

Safety culture is of paramount importance in small flight departments, where every individual's commitment to safety plays a crucial role in maintaining a safe and efficient operation. Conducting a safety culture survey tailored to the specific needs of a small flight department can provide valuable insights into the organization's safety culture. In this article, we present a selection of the best questions to include in a safety culture survey for small flight departments.
Leadership and Safety Commitment
- Do you believe that safety is a top priority for the leadership in our flight department?
- Are leaders actively involved in promoting and fostering a strong safety culture?
- Do you feel that leaders demonstrate a genuine commitment to safety through their actions and decisions?
Communication and Reporting
- Are there effective communication channels in place to address safety concerns within our flight department?
- Do you feel comfortable reporting safety incidents, near misses, or hazards to the appropriate authorities?
- Are safety concerns promptly addressed and followed up on by management?
Employee Engagement and Empowerment
- Do you feel empowered to speak up and intervene if you observe an unsafe condition or behavior?
- Are your opinions and suggestions regarding safety taken into consideration by the flight department?
- Do you have opportunities to actively participate in safety-related activities and initiatives?
Safety Training and Competency
- Have you received adequate safety training relevant to your role and responsibilities?
- Do you feel confident in your knowledge and skills to perform your job safely?
- Are there opportunities for continuous safety training and development in our flight department?
Hazard Identification and Risk Management
- Do you feel that potential hazards and risks are effectively identified and communicated in our flight department?
- Are risk assessments conducted regularly for tasks or activities with safety implications?
- Do you believe that appropriate controls are implemented to mitigate identified risks?
Learning and Continuous Improvement
- Is there a culture of learning from safety incidents and near misses within our flight department?
- Are lessons learned from safety incidents shared and integrated into safety procedures?
- Do you believe that our flight department takes proactive measures to continuously improve safety?
Safety Performance Recognition
- Are safety achievements and efforts recognized and celebrated within our flight department?
- Do you feel that safety performance is acknowledged and rewarded appropriately?
- Do you receive feedback on your safety performance and areas for improvement?
Assessing safety culture in small flight departments through a targeted safety culture survey is crucial for fostering a strong safety culture and maintaining safe operations. The questions provided in this article address key aspects of safety culture, including leadership commitment, communication, employee engagement, training, hazard identification, risk management, learning, and performance recognition. By incorporating these questions into a safety culture survey, small flight departments can gain valuable insights into their safety culture, identify areas for improvement, and implement targeted strategies to further enhance safety. Customizing and adapting the questions to suit the specific characteristics and context of the flight department will ensure accurate and actionable results, contributing to a stronger safety culture and a safer aviation environment.
###
Read More
Comparing FAA SMS Part 5 and ICAO Annex 19 Safety Management System
August 21, 2023

Safety Management Systems (SMS) are integral components of aviation organizations' efforts to enhance safety, prevent accidents, and continuously improve operational practices. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) have developed their respective guidelines for SMS implementation. This article aims to compare the FAA Safety Management System Part 5 and ICAO Annex 19 Safety Management System to highlight their similarities and differences.
FAA Safety Management System Part 5:
The FAA Safety Management System (SMS) Part 5 establishes the regulatory framework for SMS implementation in the United States. It outlines the requirements for aviation organizations, including air carriers, airports, and maintenance facilities, to establish, implement, and maintain their SMS.
Key Features of FAA SMS Part 5:
Compliance-based approach:Compliance-based approach: The FAA SMS Part 5 emphasizes compliance with regulations and standards as the foundation of a robust SMS. It requires organizations to establish safety policies, identify hazards, assess risks, implement safety risk controls, and develop safety promotion programs.
Gradual implementation:Gradual implementation: The FAA recognizes that organizations may have different levels of SMS maturity. Part 5 allows for a phased approach to SMS implementation, allowing organizations to develop their systems progressively.
Risk-based decision-making: Risk-based decision-making: The FAA SMS Part 5 encourages organizations to adopt a risk-based approach when making operational decisions. It emphasizes the importance of collecting and analyzing safety data, conducting safety risk assessments, and implementing proactive risk management strategies.
ICAO Annex 19 Safety Management System:
ICAO Annex 19 provides the global standard for the implementation of Safety Management Systems across all member states. It was developed to harmonize SMS practices and ensure a consistent approach to aviation safety worldwide.
Key Features of ICAO Annex 19:
Performance-based approach: ICAO Annex 19 adopts a performance-based approach to SMS implementation. It focuses on achieving safety performance objectives rather than prescribing specific processes or procedures. Organizations have the flexibility to develop SMS that suit their operational needs.
State's responsibility: Annex 19 places the primary responsibility for SMS implementation on the state. It requires member states to establish a regulatory framework, define safety responsibilities, conduct safety oversight, and provide support to organizations in implementing SMS.
Integration with other management systems: ICAO Annex 19 emphasizes the integration of SMS with other management systems, such as quality management and risk management. It encourages organizations to align safety processes with overall business objectives and operational practices.
While both the FAA SMS Part 5 and ICAO Annex 19 share the common goal of enhancing aviation safety through effective SMS implementation, there are notable differences in their approaches.
Regulatory Framework: The FAA SMS Part 5 provides specific regulatory requirements for SMS implementation in the United States, while ICAO Annex 19 establishes global standards without direct regulatory enforcement.
Compliance vs. Performance: The FAA SMS Part 5 focuses on compliance with regulations and standards, whereas ICAO Annex 19 adopts a performance-based approach, allowing organizations more flexibility in achieving safety objectives.
Implementation Approach: The FAA allows for a phased approach to SMS implementation, while ICAO Annex 19 requires member states to establish a comprehensive regulatory framework and oversee SMS implementation within their jurisdiction.
The FAA Safety Management System Part 5 and ICAO Annex 19 Safety Management System serve as important guidelines for aviation organizations to enhance safety and mitigate risks. While the FAA SMS Part 5 focuses on compliance and provides specific regulatory requirements, ICAO Annex 19 takes a performance-based approach and emphasizes harmonization across member states. Ultimately, the choice between these frameworks depends on the jurisdiction in which an organization operates. Regardless of the chosen framework, the implementation of a robust SMS is essential to fostering a safety culture and continuously improving aviation safety worldwide.
###
Read More
Embracing the Future: The Transformative Role of Technology in Safety Management Systems
August 1, 2023

In an ever-evolving world, the landscape of safety management systems is being reshaped by rapid advancements in technology. From artificial intelligence to the Internet of Things, innovative solutions are revolutionizing how organizations approach safety, proactively identify risks, and mitigate potential hazards. As we peer into the future, the integration of technology promises to usher in a new era of enhanced safety measures and unprecedented levels of protection.
Predictive Analytics and Risk Mitigation
One of the most significant contributions of technology to safety management systems is the emergence of predictive analytics. By harnessing the power of big data, organizations can analyze historical information, real-time data streams, and various external factors to forecast potential risks and mitigate them before they materialize. These advanced algorithms enable safety professionals to make data-driven decisions, prioritize resources, and allocate efforts where they are most needed.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Connected Safety
The IoT, a network of interconnected devices and sensors, is transforming safety management systems by creating a web of real-time information. From wearable devices that monitor vital signs and detect hazardous conditions to smart sensors that track environmental factors, the IoT enables a connected safety ecosystem. This connectivity facilitates rapid response times, enables remote monitoring, and empowers safety professionals with actionable insights for timely intervention.
Virtual and Augmented Reality for Training and Simulations
Virtual and augmented reality technologies are revolutionizing safety training and simulations. By immersing individuals in realistic, virtual environments, these technologies enable hands-on experiences without exposing workers to actual risks. Employees can practice emergency response procedures, explore hazardous environments, and develop critical decision-making skills in a safe and controlled setting. VR and AR not only enhance training effectiveness but also reduce costs associated with physical simulations.
Drones and Robotics for Risk Assessment and Inspections
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, are increasingly employed in safety management systems for risk assessment and inspections. Drones can access difficult-to-reach areas, perform inspections with high precision, and capture visual data for analysis. They eliminate the need for human workers to enter hazardous zones, thereby minimizing exposure to potentially dangerous environments. Additionally, robotics play a crucial role in automating repetitive and high-risk tasks, reducing human error and enhancing overall safety.
Artificial Intelligence for Incident Prediction and Response
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming safety management systems by enabling advanced incident prediction and response capabilities. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict potential safety incidents with a high degree of accuracy. AI-powered systems can also provide real-time recommendations for mitigating risks and assist in decision-making during emergencies. By leveraging AI, organizations can achieve a proactive and preventive approach to safety, reducing the likelihood of accidents and their associated consequences.
The future of safety management systems is inherently intertwined with technology. As organizations embrace innovative solutions, they gain the ability to anticipate, prevent, and respond effectively to safety hazards. By leveraging predictive analytics, the IoT, virtual and augmented reality, drones, robotics, and artificial intelligence, safety professionals can create an environment that fosters proactive risk management, continuous improvement, and employee well-being. As we move forward, the integration of technology into safety management systems will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in ensuring a safer and more secure future for all.
###





